
The benefits of shooting
Hugo, a young shooter passionate about sport and nature, shares his views on what the benefits of shooting really are.
Get information on the legal shooting season for mammals and birds in the UK.
Apply for funding for your project or make a donation today
Comprehensive information and advice from our specialist firearms team.
Everything you need to know about shotgun, rifle and airgun ammunition.
Find our up-to-date information, advice and links to government resources.
Everything you need to know on firearms law and licensing.
All the latest news and advice on general licences and how they affect you.
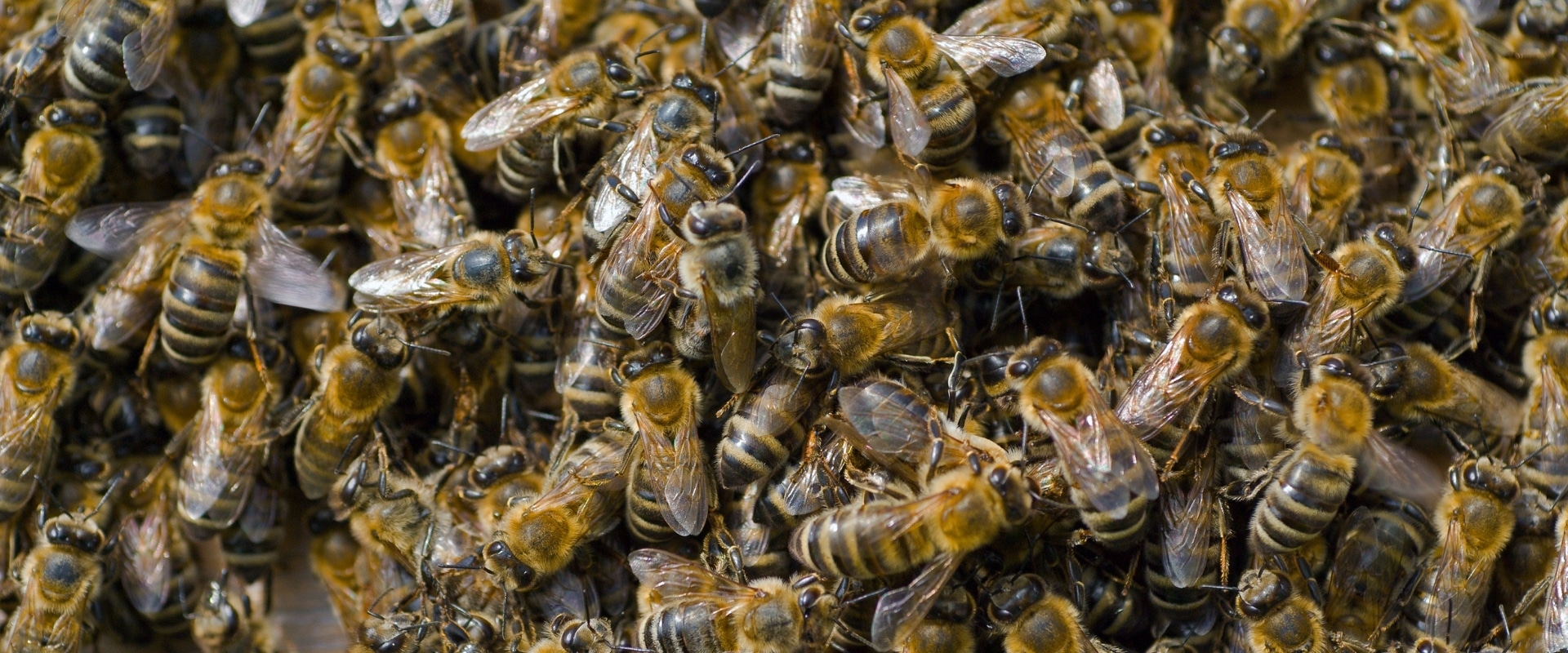

My dad and I have both become very interested in bees and beekeeping. With a friendly neighbour willing to teach us and seven hives on the go, we have everything we needed to get started. So far it has been very interesting and great fun to see everything that goes on in the hives. As keen hunters, we love to know where our food comes from, so harvesting honey is right up our alley.
If you would like to find out more about beekeeping, visit the British Beekeepers’ Association website.
Firstly, the bees need to collect the pollen and nectar. Worker bees will travel up to five miles to gather nectar! They then place the nectar in empty combs made from beeswax and dehydrate the honey by flapping their wings very quickly. After this, they create a wax to seal over the honeycomb and keep it protected.
Beekeeping is a very important job. Beekeepers not only produce the delicious honey for us to enjoy, but they also care for the bees and move the hives to help farmers in pollinating various crops, such as rapeseed fields or orchards.
If you are thinking about beekeeping, some basic knowledge of the bee is important.
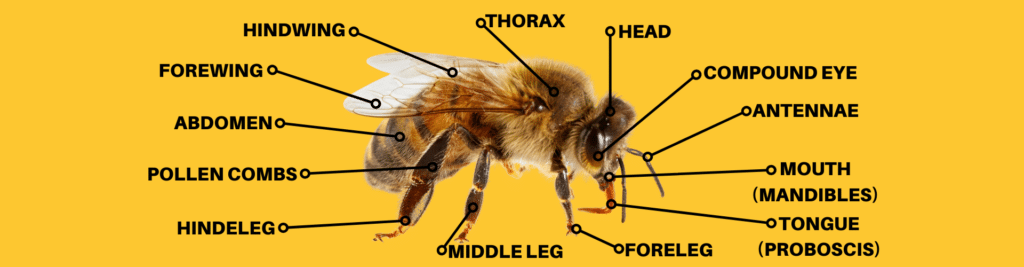
There are three main body parts to a bee: the head, the thorax, and the abdomen.
The head
is the centre for information gathering. Their senses – taste, sight and smell – also come from there. So, bees heads are very much like our own heads. Their mouth and antennae are also located at the front of their head.
The thorax
is the middle section of a bee’s body. This is where the four wings and three pairs of legs are located. The legs are very versatile; claws allow them to have good grip on rough surfaces, and a soft pad helps them walk on smooth surfaces such as grass. The pollen basket can also be found within the thorax. It is on the tibia of the hind leg, covered with tiny hairs (pollen combs) on the edges and a long central bristle that goes through the pollen pellet. This ensures the load will stay on the bee’s leg in flight. On the front leg of a bee, there is a special structure used for cleaning their antenna, aptly named the antenna cleaner!
The abdomen
is the final section of a bee. A worker, drone and queen bee can be distinguished by the size of their abdomen. Honeybees produce wax scales on their abdomen using four pairs of wax glands. The wax scales can be seen even with the naked eye. They are thin and clear, but once the workers have chewed them up and mixed them with saliva, they become whitish. The sting is another feature of the abdomen. It has barbs preventing it to be pulled out. Once a worker bee has stung someone, part of its digestive system is pulled out, killing the bee.
When bees are moved by beekeepers, they will do an orientation flight before settling back down. They fly around using the sun to navigate and figure out where they are. They can do that even on a cloudy day.
While trees and woodlands are essential to filter our air, bees are crucial to pollinating plants we all need to survive. They also pollinate many of the trees and flowers that provide habitats for wildlife. Bees have a large part to play in the ecosystem.
At least 30 per cent of the world’s crops and 90 per cent of all plants require cross pollination to propagate and thrive. Cross pollination is when pollen from one flower or plant is moved, usually by a pollinator like a bee, to another. They can help support the growth of trees, flowers, and other plants. Bees are also responsible for creation of some seeds, nuts, berries and fruits. These all serve as a food source for wild animals and us, humans, too.
A bee (like anything else) is also part of the food chain – many mammals, birds and insects prey on bees. Some of the dangerous alien invaders threaten our bees, too, such as the Asian hornet. They are the biggest threat to beekeeping but also to our dwindling wild bee populations. To help protect the bees, keep an eye out for Asian hornets – BASC has a handy guide of how to spot, ID and report them, here.
A world without bees could struggle to sustain the global human population of seven billion.
Without bees, it would be nearly impossible for life on earth to continue. They play an important role in ecology and we need to support them as much as we can whether it’s starting your own hives or just simply planting wildflowers in your garden.
You can support bees by building special insect homes for there – we have a video on how to make them, here.
You can also read more about bees and how to support them in three articles wholly dedicated to pollinators:

Hugo, a young shooter passionate about sport and nature, shares his views on what the benefits of shooting really are.

BASC Young Shots Journalist James Kinghorn considers how best to introduce the next generation to fieldsports.

Young Shots Journalist Louis went to The Game Fair to find out more about sustainable ammo and cooking game.